What is Sustainable Investing?
Jonathan Bibby
Financial Adviser Team
Sustainable investing is the practice of analysing a company's environmental, social and governance (ESG) risks, as well as assessing its opportunities and progress. This area of investing has become extremely important to consumers, organisations, and governments alike, and to help investors align their concerns for these issues with their investment philosophies, ESG funds have become available.
ESG funds have gone from being a relatively niche investment philosophy to one that is popular with investors worldwide. As investors become more concerned with the impact their investments are making in the world, ESG funds and sustainable investing practices have continued to gain traction and investors are increasingly putting their money into sustainable investments to help them meet their financial objectives. These types of funds use specific criteria when selecting their investments and assessing their impact on society. The underlying companies ESG funds select are judged on the way in which they operate as well as how well they are performing.
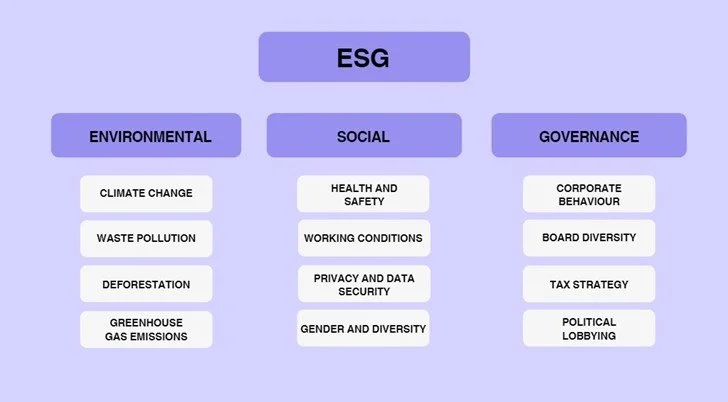
The three broad categories ESG considers when rating investments are: Environmental, Social and Corporate Governance. These are broken down further in the diagram below.
It is important to note that while sustainable investing and ESG are linked, they are not the same. Sustainability is concerned with environmental, social and economic factors; ESG on the other hand is a framework for assessing and rating the sustainability of an organisation and investment. The key distinction is that sustainable investing as a concept is vague, whereas ESG is specific and measurable.
ESG fund managers employ a wide array of methods to construct their ESG fund portfolios, however the three most common techniques are Negative Screening, Positive Screening, and Thematic Investing.
Negative Screening
Negative Screening is a technique where fund managers exclude stocks that have undesirable characteristics. Exclusion techniques may include screens that rule out investing in entire industries, for example investment in the stocks of oil companies due to their impact on the environment, or investment in tobacco companies due to their impact on social health issues. ESG funds may also exclude investment in organisations if their ESG scores fall below a certain acceptable level.
Positive Screening
Positive screening actively searches for funds to include in their portfolio, as opposed to funds or industries to exclude. Fund managers use screens to find organisations that are top performers when considering ESG ratings by external agencies. ESG funds may consider organisations with high ESG scores overall across all criteria, whereas others may seek out top performing organisations in single areas for example the Environmental aspect of ESG.
Thematic Investing
Thematic investing is where an ESG manager seeks to identify trends that have longevity and contribute well to ESG issues. For example, ESG managers may identify trends such as solar energy, electric vehicles, or online education and choose to gain exposure to organisations within each industry.
If you are thinking about holding ESG funds in your portfolio, it is important to consider some of the issues associated with sustainable investing. These include how performance is measured, efficacy in bringing about actual change, and ‘greenwashing’ (where a company makes broad sustainability claims without evidence). Therefore, doing research and carefully selecting your investments to make sure they align with your goals and investment philosophy is important.
If ESG funds and sustainable investment practices are something that interest you, we would be happy to assist you in your search. Please contact us to speak to a member of our team.
The value of investments and the income derived from them may go down as well as up.